One of the best user friendly options out there for Mac users who want to run GIS software natively is QGIS.
What is QGIS?
QGIS is an open source GIS software package that can be freely installed on a variety of computer operating systems, including Mac OS.
Anita Graser provides an overview to the QGIS ecosystem which includes a desktop GIS component, cloud hosting, and mobile application. QGIS offers compatibility for a variety of GIS vector and raster file types (such as shape files, KMLs, and GeoTIFFs) so it works well for those that need to migrate back and forth between other GIS and mapping platforms. More information about QGIS is available in the article Getting Started with QGIS.
Verify your computer’s minimum requirements
Before downloading QGIS, ensure your Mac meets the minimum system requirements. QGIS runs efficiently on macOS 10.13 (High Sierra) and later versions. You’ll need at least 4GB of RAM (8GB recommended) and sufficient space on your hard drive for installation and data storage.
Installing QGIS on a Mac
Installing QGIS on a Mac requires a few specific steps due to the macOS architecture. Apple uses Gatekeeper to determine the risk of newly installed applications on your Mac OS computer.
Since QGIS is not part of the App Store, you will need to override the safety settings on your computer. Follow the steps below to successfully install and run QGIS on your Mac computer.
Retrieving QGIS
To install QGIS on a Mac, the first thing you need to do is visit the QGIS download page to retrieve a copy of the QGIS installer. The download page provides access to the required installers and the QGIS download link for a variety of operating systems: Windows, Mac, Linux, BSD, and Android.
When you visit the download page, you will need to decide which version of QGIS you will install on your computer.
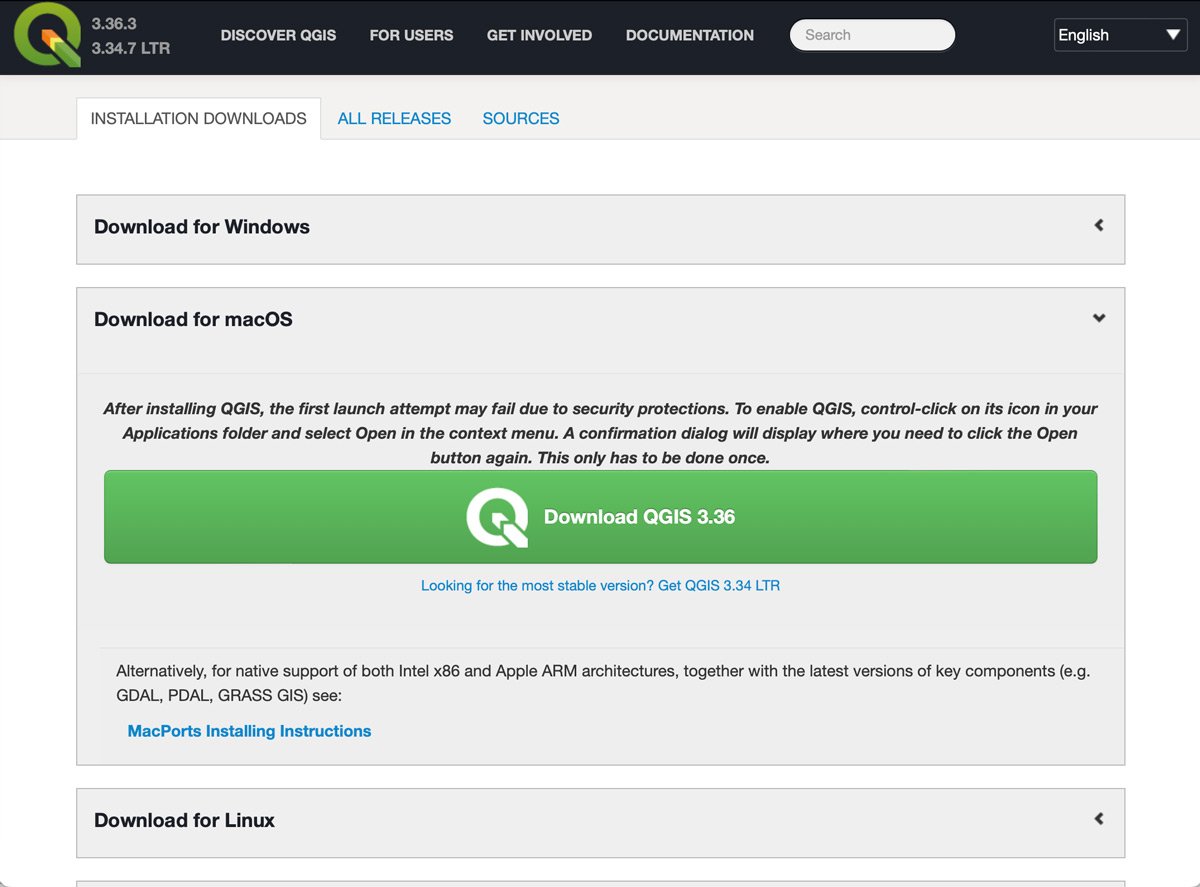
There are always two options: the most recent release of QGIS and what is known as the LTR version. LTR stands for long-term release. These LTR releases are a version of the QGIS software that are intended to be more stable and better supported over a longer period than regular releases.
The most recent release will contain more of the newer features and improvements than the LTR version. However, the newer release make contain more bugs and instability compared to the LTR version.
Installing QGIS on a Mac
Installation is pretty straightforward. Once you have selected which version of QGIS you would like to stall, click on the link and select the location on your computer where you want the .dmg file to be saved to.
On your computer, find the downloaded .dmg file and double click to start the installation process. Once the installation has been verified by Mac OS, you will be presented with the licensing agreement interface.
QGIS relies on several open-source packages and libraries to function properly, which are often bundled with its installation. These dependencies provide various functionalities, from data rendering to spatial analysis. Some of these open-source packages and libraries that typically install with QGIS are:
- GDAL/OGR: The Geospatial Data Abstraction Library (GDAL) is used for reading and writing raster geospatial data formats, while OGR is used for vector formats. Together, they support numerous geographic data formats and provide functionalities like transformation and reprojecting spatial data.
- PROJ: This library is responsible for performing cartographic projections and other coordinate transformations. It’s essential for ensuring that spatial data from different sources and projections can be used together accurately.
- SQLite/SpatiaLite: SQLite is a lightweight database system that QGIS uses for various internal functions. SpatiaLite extends SQLite to support spatial data types and operations, enabling spatial queries and GIS operations directly within a SQLite database.
- PostgreSQL/PostGIS: While not necessarily installed automatically with QGIS, QGIS supports connections to PostgreSQL databases with PostGIS extensions, which add support for geographic objects allowing spatial queries.
- Qt: This is a cross-platform application framework that QGIS uses to manage its graphical user interface. Qt provides tools for developing applications with graphical user interfaces in C++.
- Python: QGIS includes a built-in Python interpreter to support scripting and automation within the software. Python allows for the extension of QGIS functionalities through scripts and custom plugins.
- GRASS GIS: Often bundled with QGIS, especially in advanced installers, GRASS GIS is a powerful open-source GIS software that provides QGIS additional analytical capabilities, including complex geoprocessing and modeling.
To continue with the install, click on the “Agree” button to accept the open source licensing agreement for QGIS.
Move the QGIS install to the Applications folder
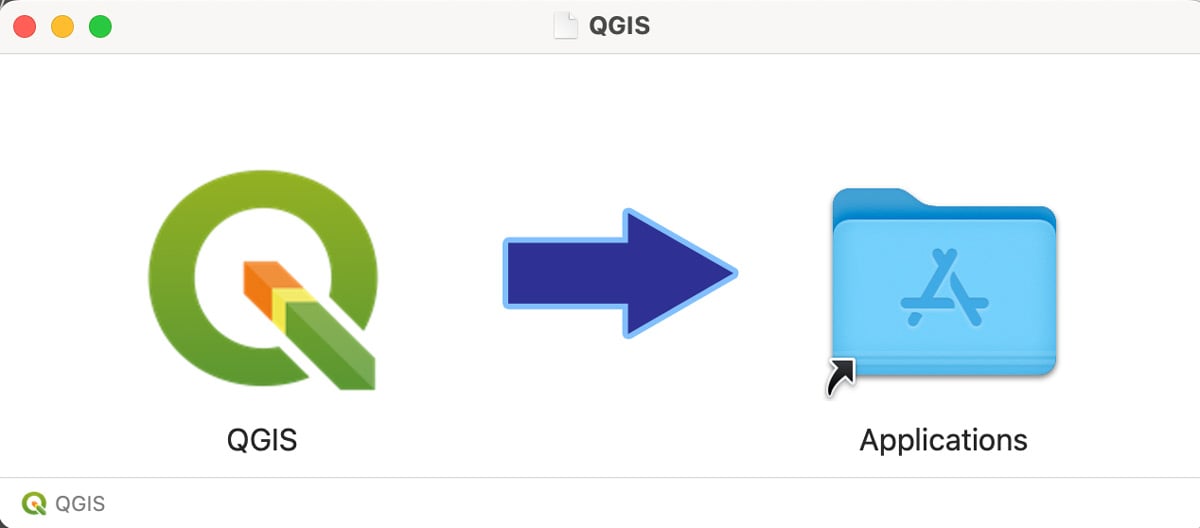
Once you have agreed to the licensing requirements, you will be presented with instructions to drag and drop the QGIS icon into the Applications folder:
If you already have a version of QGIS installed in the Applications folder, you will be asked if you want to keep both versions or replace the version of QGIS. If you are simply wanting to upgrade to a newer version of QGIS, then select the “Replace” button. If you are interested in running different versions of QGIS, for example both the most recent and LTR versions, then select the “Keep Both” button.
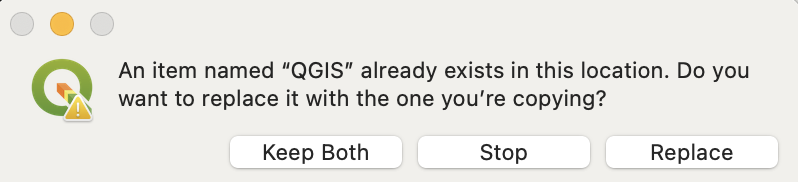
Once you make your select, then the QGIS bundle of software will be copied into the Applications folder. A status interface will run until the installation is complete:
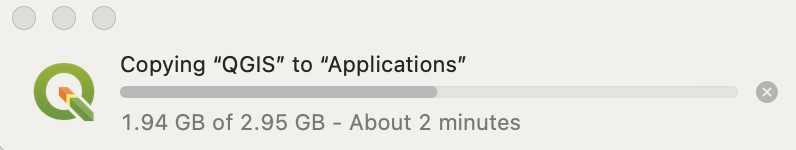
Once the copying of QGIS into the Applications folder is complete, you can launch the software. The first time you try to open a newly installed version of QGIS, the Mac OS’ Gatekeeper system will issue a warning. Follow theses steps to allow QGIS to run on your Mac computer.
Overriding Mac Security Preferences to Install QGIS
To launch QGIS for the first time, open Finder. Then on the left side of the Finder panel, location the Applications icon and click it. From the list of Applications in the right panel, locate the QGIS icon.

Normally, to run a software program on a Mac computer, you would double-click the icon to launch it. When you do the first time with QGIS the following will happen:
Gatekeeper will try to verify the installation of QGIS. Once it can’t a pop-up will display the following message: ““QGIS” cannot be opened because the developer cannot be verified. macOS cannot verify that this app is free from malware.”
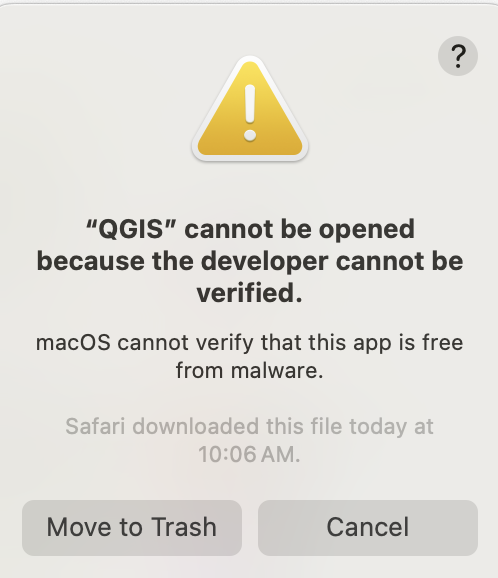
To allow QGIS to run on your Mac OS computer, you will need to manually override this security setting by following these steps:
- In the applications folder, right click on the QGIS icon.
- Select “Open” from the menu options.
- This will trigger a new warning popup that now includes the option to open QGIS anyway:

- Select “Open” to continue the launch of QGIS.
- You will only need to do this once. Selecting “Open” modifies the security settings for your Mac to allow future launches of QGIS to proceed without the security warning. The next time you double-click on the QGIS icon, the software will simply open up.
Add the QGIS Startup Icon to the Dock
For a quicker startup of your QGIS installation, add the QGIS icon to the Dock on your Mac. To do so, open up Finder and click on the Application shortcut. Find the QGIS icon and select it. Now drag it using your mouse to the dock and drop the icon where you want it to show up. You will be able to drop it in place when you see the existing icons on the Dock separate.
Now, when you want to start QGIS, simply click on the icon from the Dock.
Cleanup: Remove QGIS installer file from your computer
Once you have successfully installed QGIS, you no longer need the installer file. Find the QGIS .dmg file and move it to your computer’s trash can. Empty the trash can to recover the storage space taken up by the roughly 1.6 GB QGIS installer file.
You should also eject the QGIS installer file from the Finder’s locations section by clicking the icon next to the QGIS installer name to unmount it.

Video Tutorial: How to Install QGIS on the Mac for versions 2.x and 3.x
If you prefer, this tutorial is available as a video:
UPDATE: The instructions in this video no longer apply for installing QGIS 3.x versions on newer Mac OS versions.
QGIS Mac Tips
Associating QGIS File Types
QGIS projects are saved with the .qgs extension. Older versions of QGIS may have the .qgis extension. To associate the older extension type so that double clicking the file automatically opens up QGIS do the following: highlight the file and then click on it to open up the options. Then select Open With -> Other… Browse through the applications to find the QGIS icon. Select the icon, check the box at the bottom that says “Always open with” and then click the open button. All future instances of opening a file with the .qgis extension should now automatically start up QGIS.
Clearing Out Imported QGIS Styles
If you have hundreds of imported QGIS styles and want to clear out the imported styles without having to delete them one by one from within QGIS, you can clear out the settings from the hidden folder for QGIS found in the home direction. Access this folder in Finder by clicking the Go menu and choosing Go to Folder. Then type in ~/.qgis and click Go (backing up any files within this folder before deleting or changing them is strongly recommended).
This article was originally written on June 27, 2017 and has since been updated to reflect more recent QGIS installation instructions.


