Physical Geography
Physical geography focuses on geography as an Earth science (and is sometimes called Earth System Science).
Physical geography is a branch of geography that focuses on the study of the natural features and processes of the Earth’s surface. It includes the examination of landforms, climate, vegetation, soils, and water resources. Physical geographers use a range of scientific methods and tools to analyze and understand the complex interactions between the Earth’s physical systems.
Learn about the different branches of geography that fall under the physical geography category: climatology, geomorphology, biogeography, and more.
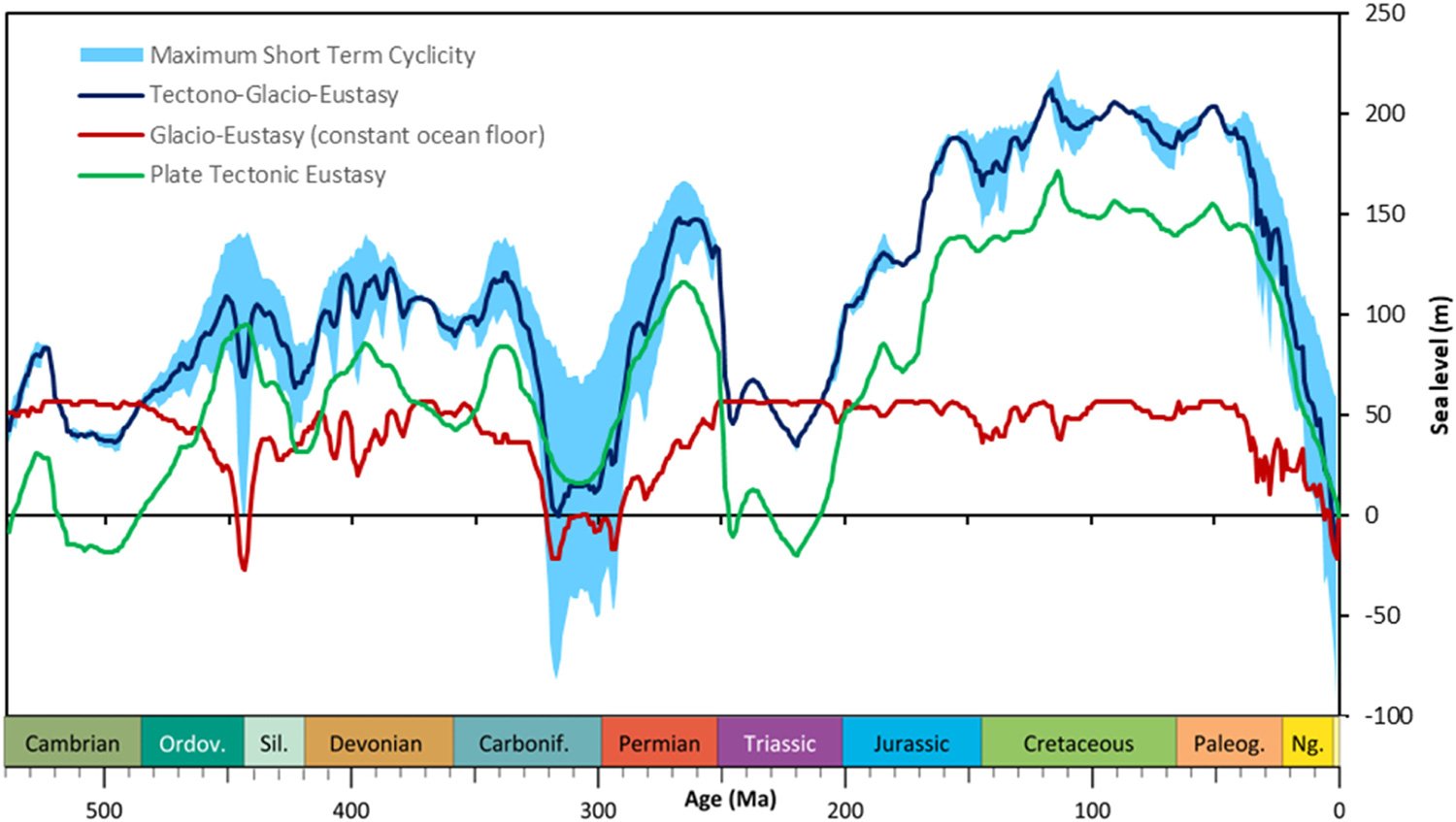
Mapping Short-term Sea Level Changes Over 540 Million Years
Study maps 540 million years of sea level change, showing major short-term shifts during ice ages driven by Earth's orbital cycles.

Water Can Take Years to Seep out of Mountains
Groundwater stored over many years is a significant contributor to streamflow in Western United States mountains according to a published study.

Study Models How the Behavior of Waves Affects Blue Carbon Storage
Bubbles created by the movement of waves can influence how much carbon dioxide is absorbed by the ocean.
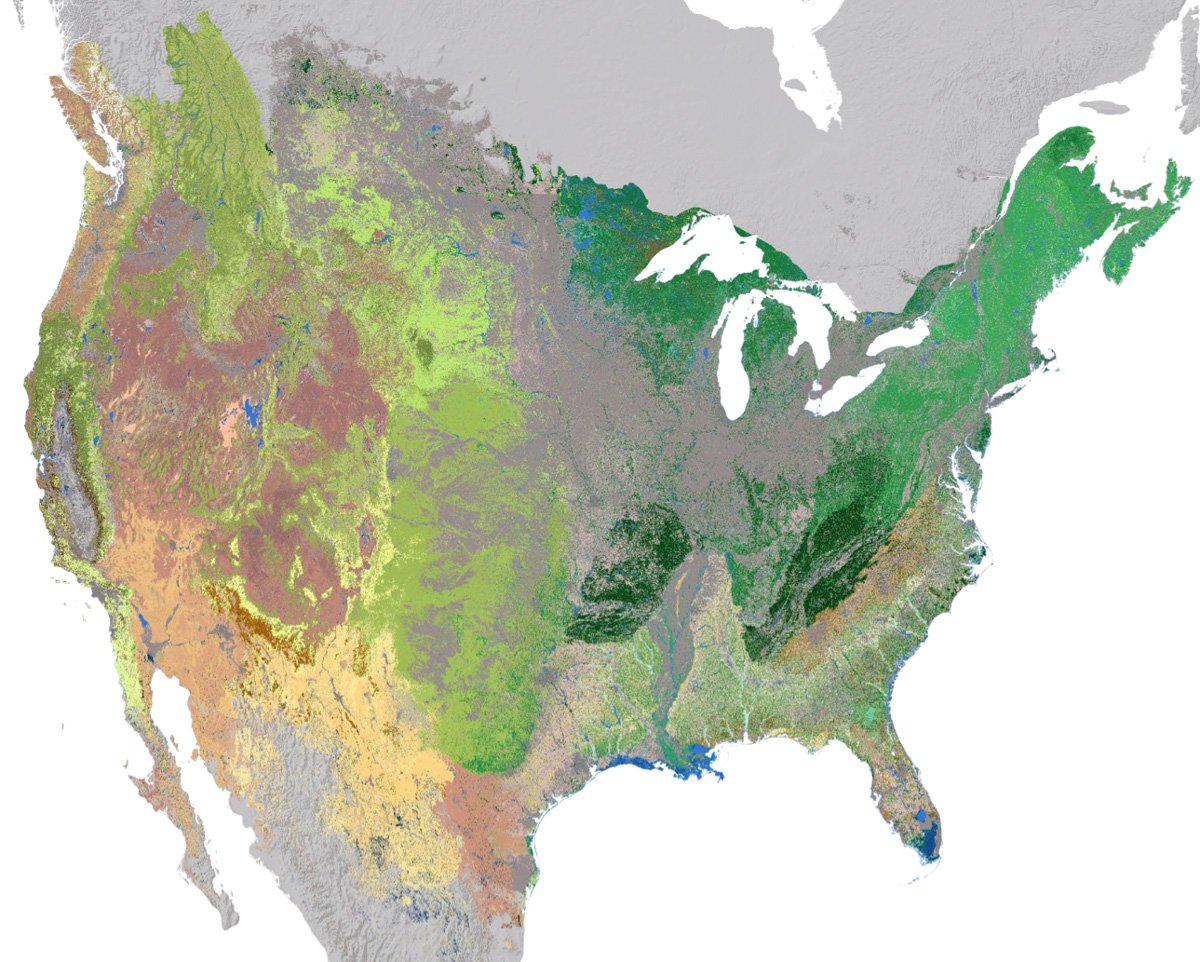
High Resolution Ecosystem Map of the Contiguous United States and Adjacent Areas
NatureServe has developed an updated 30-meter hexagon map of regional ecosystems in the contiguous United States and adjacent areas.
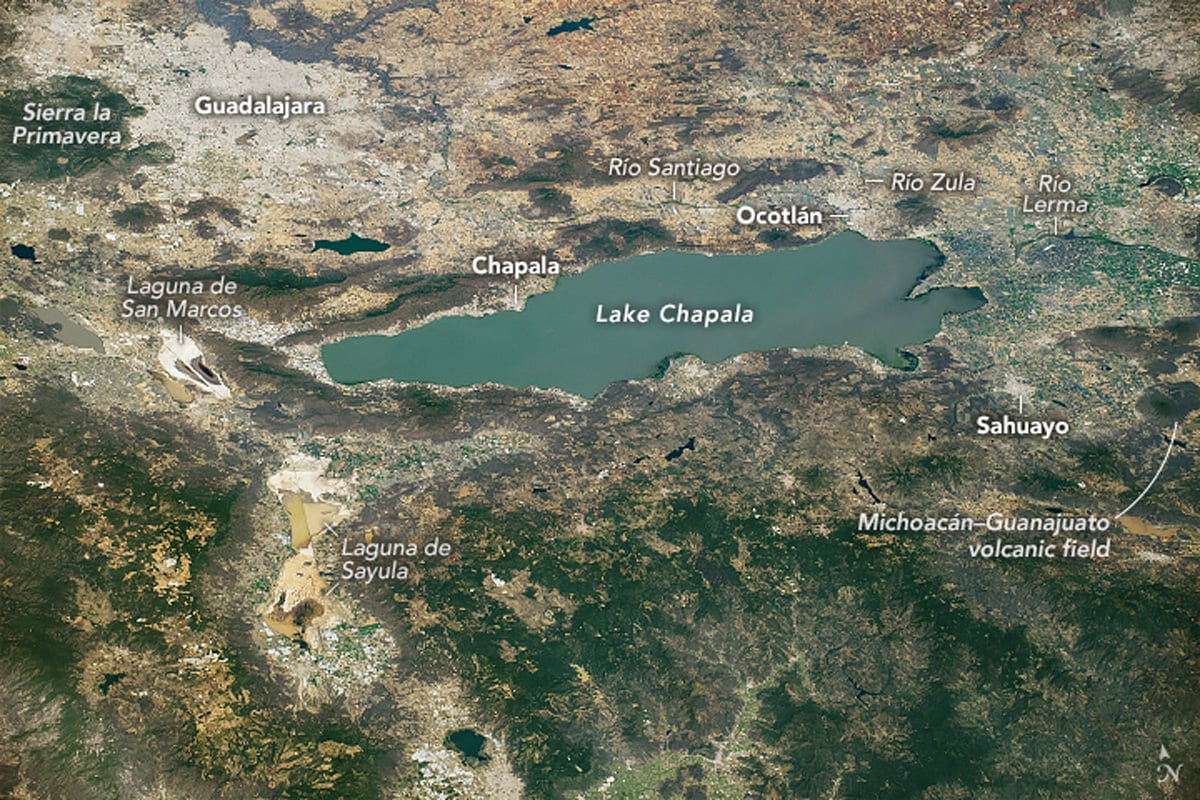
Lake Chapala: a Tectonic Lake at Mexico’s Triple-graben Intersection
Lake Chapala was formed at the intersection of three grabens.

Rivers that Flow Backwards
Read about how the Amazon once flowed east to west and how the strength of Hurricane Isaac once change the course of the Mississippi river.

World’s Biggest Iceberg
The largest iceberg in the world is A-23A, with an area of about 1,240 square miles.

Satellite Imagery of Clouds
Listed here are different clouds formations as seen on satellite imagery.

Water on Earth
Earth holds trillions of tons of water, mostly in oceans. Only 2.5% is freshwater, primarily found in glaciers, groundwater, lakes, and rivers.

Defining How Much of the World is Covered by Forests
With no universal definition, mapping and comparing forest coverage around the world is challenging.

Glacial Flour Makes Some Lakes Turquoise
Glacial flour, the fine dust created as glaciers move over land, turns lakes a turquoise color by reflecting blue and green light.

Hydroclimate Whiplash: the Impact on California Wildfires
Hydroclimate whiplash - the rapid swing between drought and heavy precipitation - plays a role in the increasing intensity of California wildfires.

Understanding Glacier Grounding Lines
Grounding lines are the boundaries where glaciers and ice sheets transition from resting on solid ground to floating on seawater.

Increased Light Pollution in the Arctic
Satellite data shows rising Arctic nighttime lights, driven by growing industrial activity in oil, gas, and infrastructure.

The Rise of Proglacial Lakes
Glacial retreat in Alaska's Yakutat Foreland has fueled rapid growth of proglacial lakes, doubling their size in 40 years as seen in Landsat imagery.

Largest Piedmont Glacier in North America
The largest piedmont glacier in North America is found in southeastern Alaska and is known as the Malaspina Glacier.

Lenticular Clouds
Lenticular clouds are lens-shaped formations that form over mountains when moist air cools and condenses, creating smooth, often UFO-like cloud patterns.

Understanding the Increase in PyroCbs: Wildfire Thunderstorms
Fire-triggered thunderstorms called pyroCbs, short for pyrocumulonimbus clouds, is on the rise.

Barrier Islands in the United States
Barrier islands are narrow landforms running parallel to coastlines, protecting shores from storms and erosion while supporting unique ecosystems.

Number of “Dees” in a Chickadee’s Alarm Call is Related to the Danger Level of Nearby Predators
The number of "dees" in a chickadee's alarm call correlates with the size and threat level of the predator.

Tracking Mercury With Dragonflies
Published research mapped mercury levels in dragonfly larvae from 73 U.S. parks, revealing how the metal accumulates in the environment.

How Undular Bores Show Up in the Clouds
Undular bores create distinctive wave-like cloud patterns, such as morning glory clouds, by pushing warm air upward.

Geography of Giant Sequoias
Giant sequoias are one of the longest lived tree species, with the oldest giant sequoia living an estimated 3,400 years.

Urbanization is Shortening the Legs of Western Fence Lizards
Western fence lizards have adapted to manmade surfaces in urban areas by developing shorter limbs and toes.

Most Abundant Landbird in the United States and Canada
The American robin has the largest population among all landbirds in the United States and Canada.

Which States Have the Highest Percentage of Water Area?
Water shapes U.S. states' geography and ecosystems. Which states have the highest and lowest percentages of area covered by perennial water?
