Physical Geography
Physical geography focuses on geography as an Earth science (and is sometimes called Earth System Science).
Physical geography is a branch of geography that focuses on the study of the natural features and processes of the Earth’s surface. It includes the examination of landforms, climate, vegetation, soils, and water resources. Physical geographers use a range of scientific methods and tools to analyze and understand the complex interactions between the Earth’s physical systems.
Learn about the different branches of geography that fall under the physical geography category: climatology, geomorphology, biogeography, and more.

Mapping Coral Reef Health with Sound
Scientists used artificial intelligence and passive acoustic monitoring to assess coral reef health by analyzing the sounds of the ocean.

A Guide to the Geography of U.S. National Parks
Find out the answers to geography trivia questions and more in this article about the geography of U.S. National Parks.

Nunataks: Glacial Islands
Nunataks are isolated mountain peaks visible above ice sheets in polar and high-altitude regions.

What is an Ice Arch?
An ice arch forms when sea ice buckles under pressure, creating a natural arch-shaped structure in polar regions, often blocking the movement of ice.

Polynyas: Natural Openings in Polar Ice
Explore the geography of polynyas, unique open water areas in polar ice, and learn about their formation, ecological impact, and role in climate dynamics.

Tracking Penguin Colonies Through Their Droppings
Researchers are using satellite imagery to map Antarctica’s penguin population by estimating their numbers based on the large guano stains left behind.

When Rivers Become Ice Roads
During the cold winter months, parts of Canada's Mackenzie River become a ice road that trucks up to 22,000 pounds can navigate.

Will Cool Air Pooling Protect Some Forests from Climate Change?
Researchers looked at the link between cool air pooling and cold-adapted forest composition.

Forecasting Phytoclimates
A study of 135,153 vascular plant species predicts that by 2070, 33-68% of land on Earth will experience significant phytoclimate changes.

The World’s Smallest Mountain Range
Located about 55 miles north of Sacramento in Northern California, this small volcanic formation is known as "the world's smallest mountain range."

Human-Driven Extinction of Birds
Researchers using models and historical records estimate that up to 11% of all bird species have gone extinct since the Late Pleistocene.

This Bird is Not the Only Crested Jay West of the Rocky Mountains
Since the 1960s, blue jays have gradually extended their range past the Rocky Mountains into the western United States and Canada.

Weather Forecasting Using Artificial Intelligence
GraphCast is a Google DeepMind effort that uses deep learning to improve medium-range weather forecasting.

Measuring Tree Height With a Two-Satellite Constellation
Researchers used synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data from colocated satellites to estimate tree canopy height.

Using Animals to Collect Weather Data
Scientists suggest using sensors on wildlife to collect fine-grained weather data about the environments these animals move around in.

How Sea Level Rise Will Affect Salt Marshes
Researchers have calculated that about 90 percent of salt marshes are under threat from rising sea levels predicted to occur by the year 2100.

American Chestnut: the Struggle to Save the ‘Redwood of the East’
Scientists and conservationists are working to rescue the American Chestnut from going completely extinct.

Surge Flows: A Rare River Phenomenon
Surge flows are a rare phenomenon where shallow waters, sand or sediment, and steep topography combine to create waves in rivers.
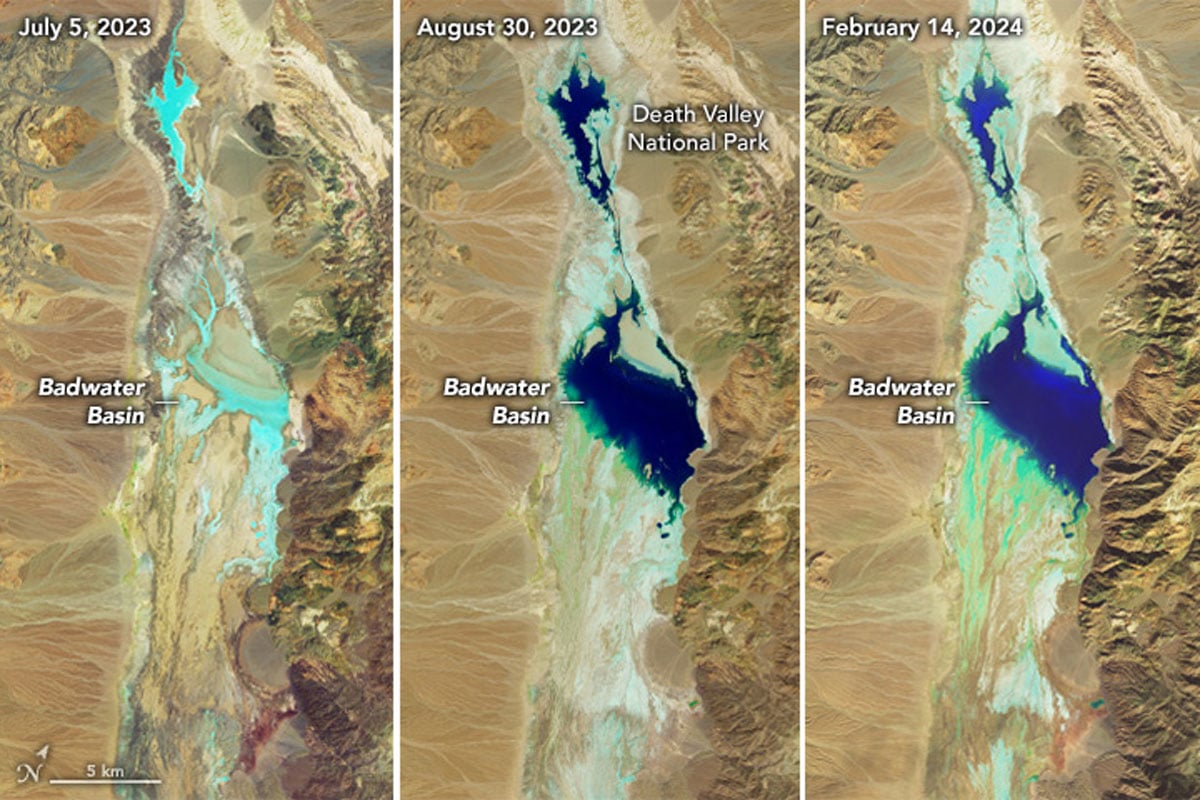
North America’s Lowest Point on Land is Currently a Lake
Two recent heavy rainfall events have filled Badwater Basin, the lowest point in North America on land, up with water.

Geography of Lightning Strikes in the United States
Researchers recently mapped out data from the U.S. National Lightning Detection Network (NLDN) between 2017 and 2022 to see where lightning strikes the most across the contiguous United States.

Why Climate Change is Making Some Animals More Nocturnal
Increase daytime heat linked to climate change is driving some wildlife to become more active at night.

Individual Seabird Adaption to Climate Change
Scientists tracked the migratory patterns of 145 seabirds to map how individual shearwaters are adapting to climate change.

Geography of Atolls
Atolls are ring-shaped coral reefs, islands, or a series of islets that encircle a lagoon either partially or completely.

The Role of Secondary Forests in Reducing Atmospheric Carbon
Secondary forests play an important role in carbon capture strategies aimed towards reducing atmospheric carbon.

Using GIS to Map an Individual Animal’s Home Range
GIS can be used to map the estimated home range based on the collected point locations of individual animals as they move through an environment.

What is the Outlook for California’s Atmospheric Rivers?
During the winter months, atmospheric rivers carry enormous amounts of water to the state of California.
