Oceanography
Oceanography is the study of the biological and physical properties of the world’s largest bodies of water, the oceans.
Oceanography is a branch of Earth science and geography that studies the oceans, including their physical and biological aspects, as well as the interactions between the oceans and the atmosphere, land, and other bodies of water. It involves the study of ocean currents, waves, tides, temperature, salinity, and other physical characteristics, as well as the diverse array of marine life that inhabits the world’s oceans.
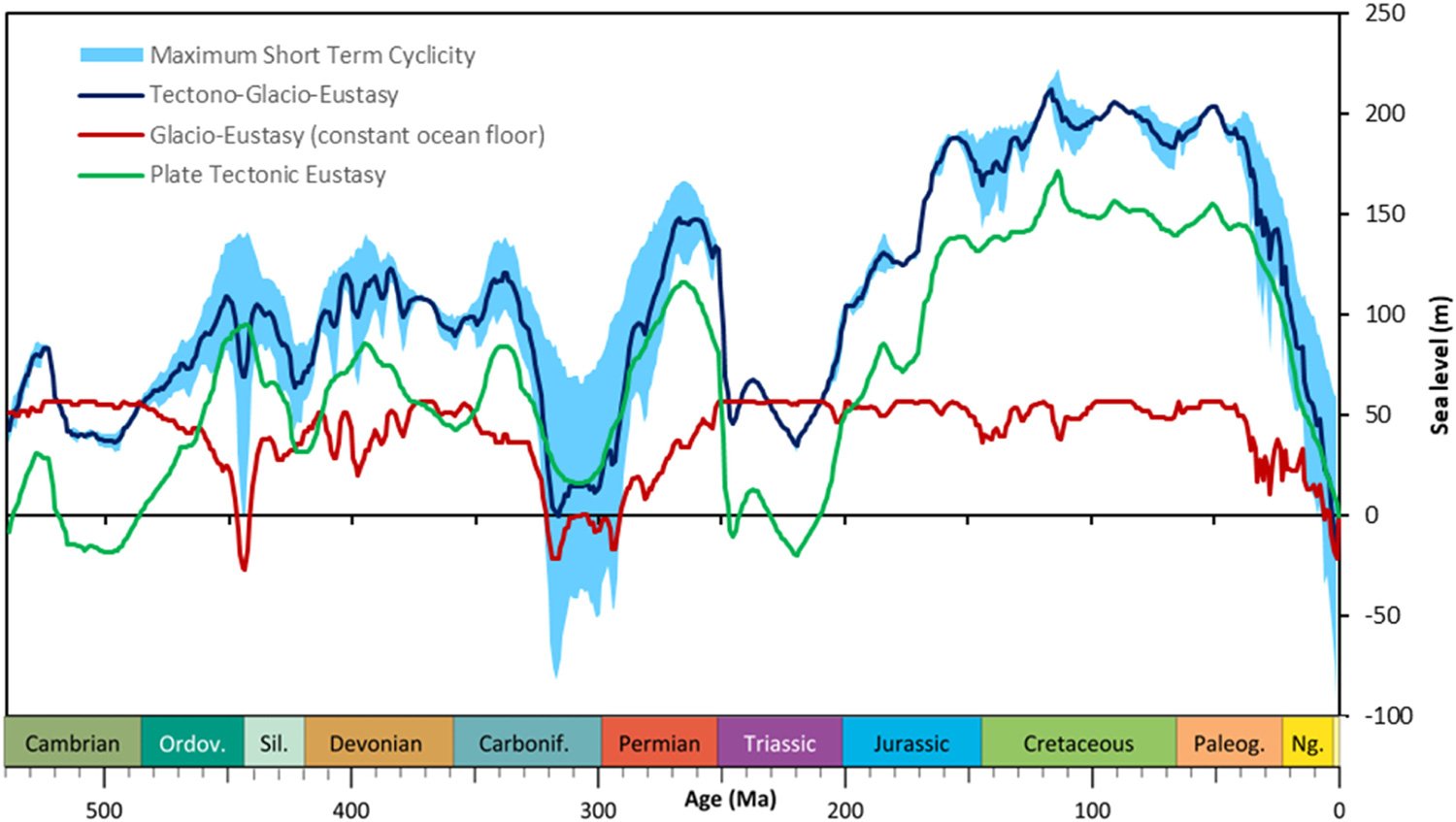
Mapping Short-term Sea Level Changes Over 540 Million Years
Study maps 540 million years of sea level change, showing major short-term shifts during ice ages driven by Earth's orbital cycles.

Study Models How the Behavior of Waves Affects Blue Carbon Storage
Bubbles created by the movement of waves can influence how much carbon dioxide is absorbed by the ocean.

Mapping Coral Reef Health with Sound
Scientists used artificial intelligence and passive acoustic monitoring to assess coral reef health by analyzing the sounds of the ocean.

Polynyas: Natural Openings in Polar Ice
Explore the geography of polynyas, unique open water areas in polar ice, and learn about their formation, ecological impact, and role in climate dynamics.

Geography Facts About the Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean is the Earth's windiest, southernmost ocean and plays a vital role in Earth's environmental health.

Marine Spatial Planning Index
The goal of marine spatial planning (MSP) is to balance ocean space use and environmental protection.

The Role of Internal Waves in Climate Change
Scientists from the UK and US have identified underwater internal waves as crucial in understanding and addressing climate change.

Warmer Ocean Temperatures are Bleaching Coral Reefs
Higher ocean temperatures, along with overfishing and pollution, are leading to more coral bleaching events.

Phytoplankton Blooms in the Northeast Pacific Ocean
During summer in the Northeast Pacific Ocean, phytoplankton blooms proliferate due to the nutrient-rich upwelling along the continental shelf.

Potential Collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation
A new study predicts that the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) could potentially collapse within this century.

Sargassum in the Atlantic Ocean Reaches a New Spring High
Researchers using remote sensing data from NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites have measured the largest ever March density in the Great Sargassum Belt.

What is the Difference Between a Sea and an Ocean?
A look at the geographic definitions of oceans and seas.

Oceans Produce Half of the World’s Oxygen
The oceans produce over half of the oxygen in the Earth's atmosphere, making them a vital source of oxygen for life on our planet.

Geography Facts About the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean, named after the Greek god Atlas, is the second-largest ocean in the world.

53% of U.S. Ocean, Coastal, and Great Lakes Waters are Unmapped
According to a new report by the United States' federal Interagency Working Group on Ocean Coastal Mapping, 53 percent of the country's ocean, coastal, and Great Lakes water is still unmapped.

How Ocean Currents Move Pollution Around the World
How does pollution from plastic, trash, and oil spills move around Earth's oceans?

How Much Would the Ocean Rise if Everyone Sat in it?
If everyone in the world decided to sit in the ocean all at once, how much would the sea level rise?

How Many Oceans are There in the World?
The world is made up of: one global ocean, three major oceans, four historic oceans, and five world oceans.

What is the Largest Island in the Pacific Ocean?
New Guinea is the largest island in the Pacific Ocean.

Lowest Latitude Sea Ice South of the Arctic
One of the lowest latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere where sea ice forms in the Northern Hemisphere is the Sea of Okhotsk.

Oceans Are Warming 40 Percent Faster Than Previously Estimated
A review of available studies, published in Science in January 2019, has revealed that the rate of ocean warming is as much as 40% faster than that suggested by IPCC.

Geography Facts About the Pacific Ocean
Learn some geography facts about the world's largest ocean.

Malvinas Current
The Malvinas Current is a cold water current that flows northward along Patagonia's Atlantic coast.

How Much Carbon Dioxide are the Oceans Absorbing?
New research shows that the world's oceans, which cover 70% of the planet, absorb more carbon dioxide than previously thought.

Gulf of Mexico Remains the Second-largest Low-Oxygen Dead Zone on Earth
A newly released forecast by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has predicted that the Gulf of Mexico will again become the second-largest low-oxygen dead zone on after (after the Baltic Sea).

Stokes Drift Is Pushing Microplastics Towards the Arctic
A recent publication in JGR Oceans took a look at how the physical processes of oceans affect the distribution of micro plastics around the world.
