Geography Basics
Geography is the study of the Earth’s physical and human features, their spatial relationships, and the processes that shape them. It is a broad and interdisciplinary field that incorporates elements of natural science, social science, and the humanities.
Geographers seek to understand the complex interactions between the natural environment and human societies, and the ways in which these interactions vary across different regions and cultures.
This category contains articles about introductory concepts in geography. Find resources, books, lesson plans, and maps for teaching geography to all ages. A fun way to learn about geography is through the use of quizzes which are also listed in this category.
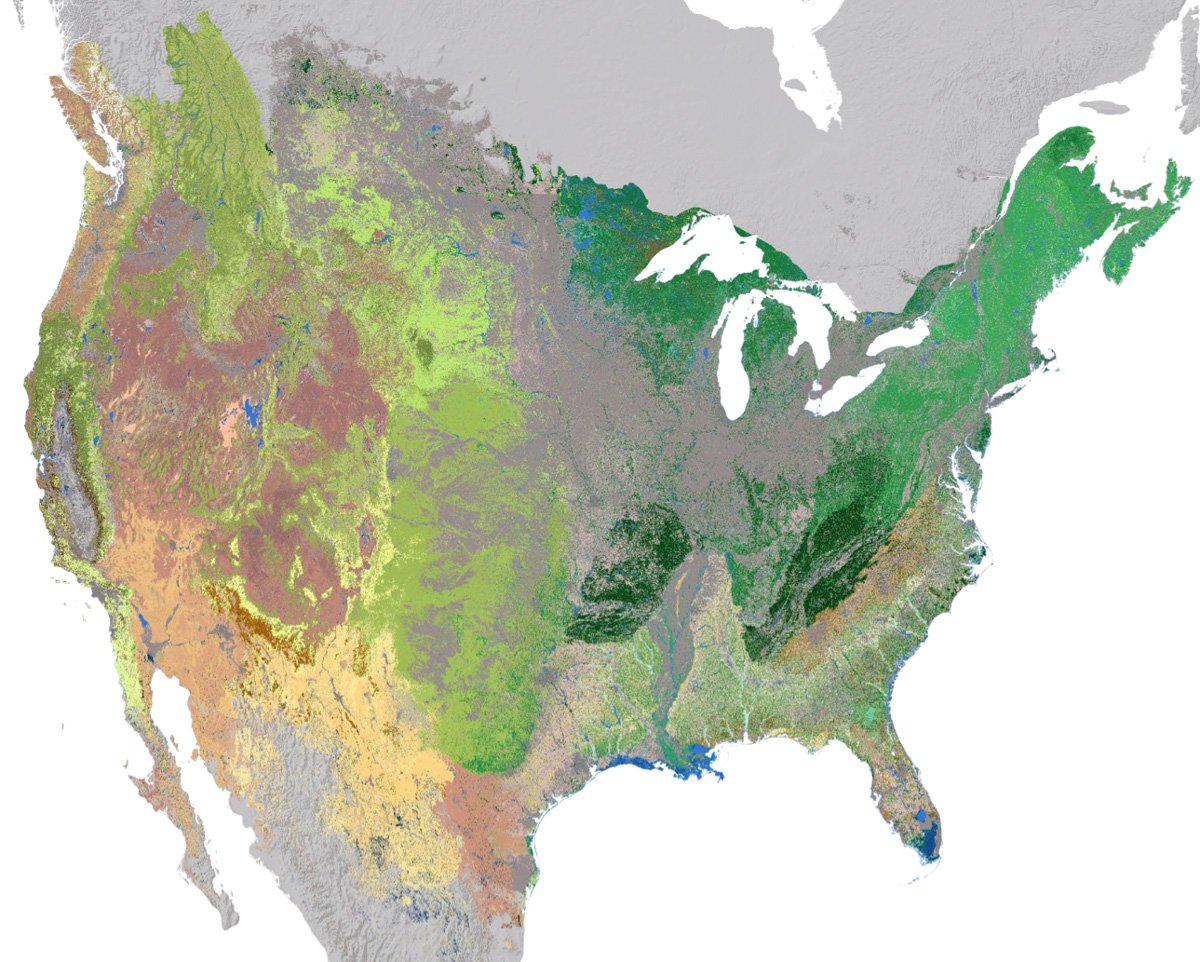
High Resolution Ecosystem Map of the Contiguous United States and Adjacent Areas
NatureServe has developed an updated 30-meter hexagon map of regional ecosystems in the contiguous United States and adjacent areas.
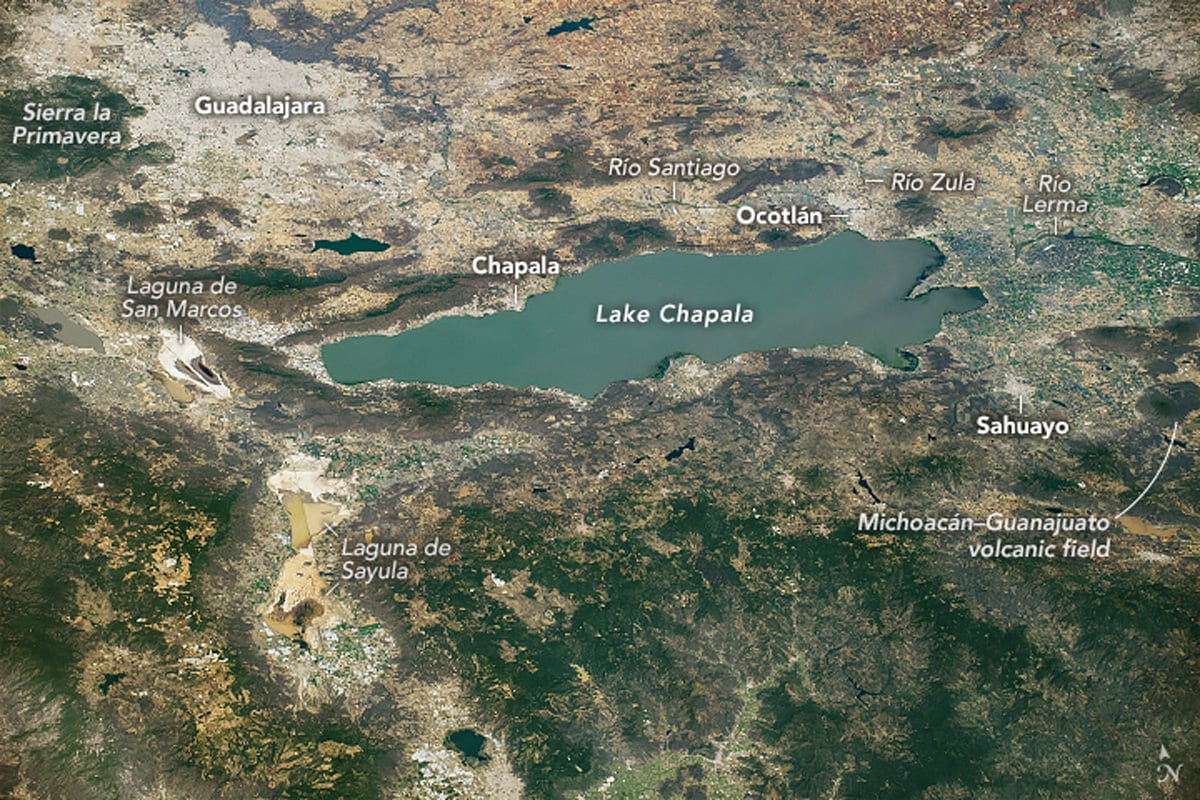
Lake Chapala: a Tectonic Lake at Mexico’s Triple-graben Intersection
Lake Chapala was formed at the intersection of three grabens.

Northernmost Point in the United States
Above the Arctic Circle, Point Barrow is the northernmost point in the United States.

How to Create a Radial Flow Map Using QGIS
Learn how to create a radial flow map in QGIS to visualize migration using metro-to-metro data from the U.S. Census Bureau.

Only State… Geography Facts
Here are some interesting geography facts that are unique to individual U.S. states and do not occur in any other state.
