Extracting objects such as trees and building footprints from high-resolution imagery has great potential to provide valuable insights for a range of applications such as city planning, environmental monitoring, and disaster management. However, the process is a challenging task that requires significant time, effort, and expertise.
In recent years, deep learning tools such as Deepforest and MaskRCNN have shown promising results in object detection in satellite and aerial imagery. These tools can automate the detection process, reducing the reliance on manual labor and human expertise.
Learn to use deep learning tools in ArcGIS Pro
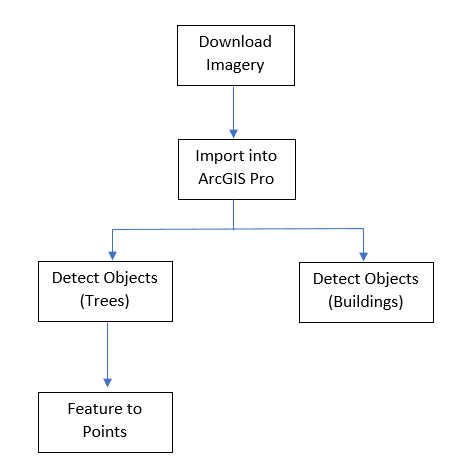
This tutorial will outline the steps involved in using these deep learning tools that have been pre-trained to extract trees and building footprint data from Google satellite imagery in ArcGIS Pro. Figure 1 shows a summary of the methodological flow employed in the tutorial to use deep learning tools to extract building footprints and trees from high-resolution imagery in ArcGIS Pro.
Finding high-resolution imagery
Retrieving high-resolution imagery from the USGS
High-resolution imagery can be retrieved from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Earth Explorer’s website after a free registration. First sign up via the EROS Registration System. Once you are registered, sign into USGS Earth Explorer’s database to access a wide range of satellite imageries and high-resolution imagery. This helpful video explains the process for signing up for USGS Earth Explorer’s website and accessing its products.
Retrieving high-resolution imagery from Google
For this tutorial, high-resolution Google satellite imagery was retrieved using a QGIS plugin by following the steps outlined:
- You will need to install QGIS on your computer. QGIS is a free-open source mapping software that produces a wide range of options for geospatial analysis of vector and raster datasets.
- Open and create a new project in QGIS by selecting “New” from the “Project” tab of the menu bar.
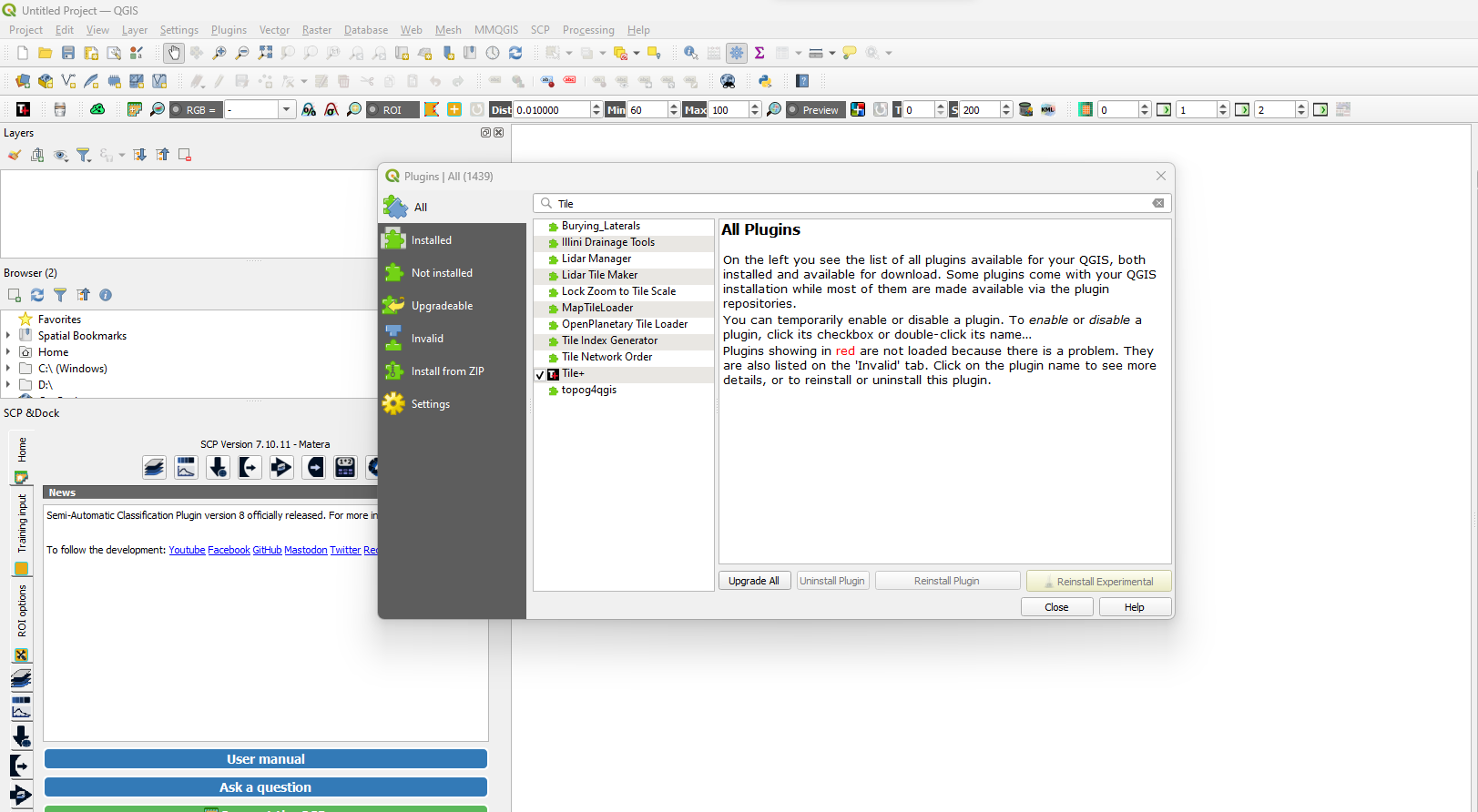
- From the plugins tab, select “Manage and install plugins.”
- Select “All” from the wide range of window options.
- Type and search Tile+ from the plugins’ search bar.
Click on the Tile+ plugin and select install plugin.
Alternatively, the Tile+ plugin can be retrieved from the web and imported into the QGIS map canvas. To use this option;
- Retrieve the plugin from the Tile Plus Plugin in QGIS web page.
- From the Plugins tab from the menu bar in QGIS, select “Manage and install plugin.”
- Select “Install from Zip” from the range of options.
- Select the three-dots beside the search bar to toggle to the downloaded Tile+ file.
- Click Install plugin.

Once the Tile+ plugin is installed, the Tile+ icon displays. Now you can use the QGIS plugin to retrieve a high-resolution Google satellite imagery for an area of interest using the steps outlined:
- Click the Tile+ icon as shown in figure 4 below.
- Set the “Select Map” tab to Google Satellite from the Tile+ window.
- Click the plus sign to display the Google satellite map onto the canvas. Zoom into an area of interest.

- Right-click on the Google satellite layer from the layers tab.
- Select Export.
- Select Save as.
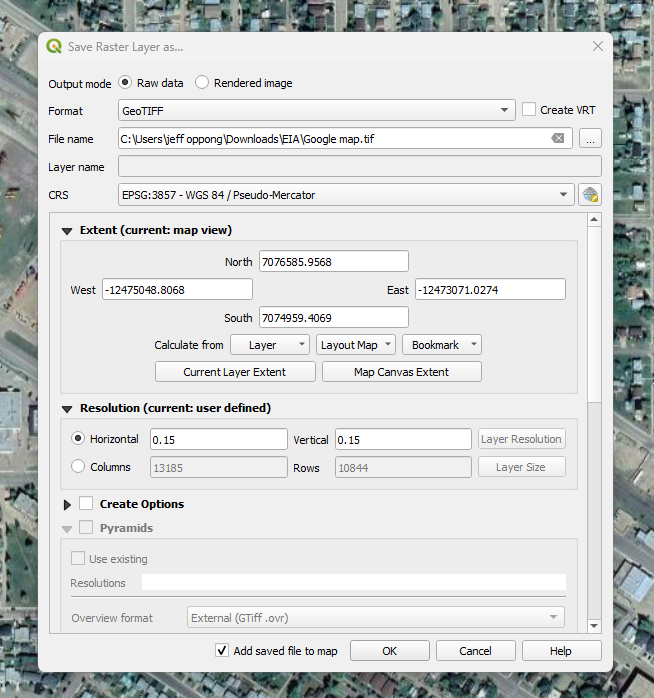
- From the Save as window, set format to GeoTIFF and uncheck “Create VRT.”
- Set File name to your desired output name and location and select “Map Canvas Extent.”
- Be sure to set horizontal and vertical resolution to 0.15.
- Click Ok.
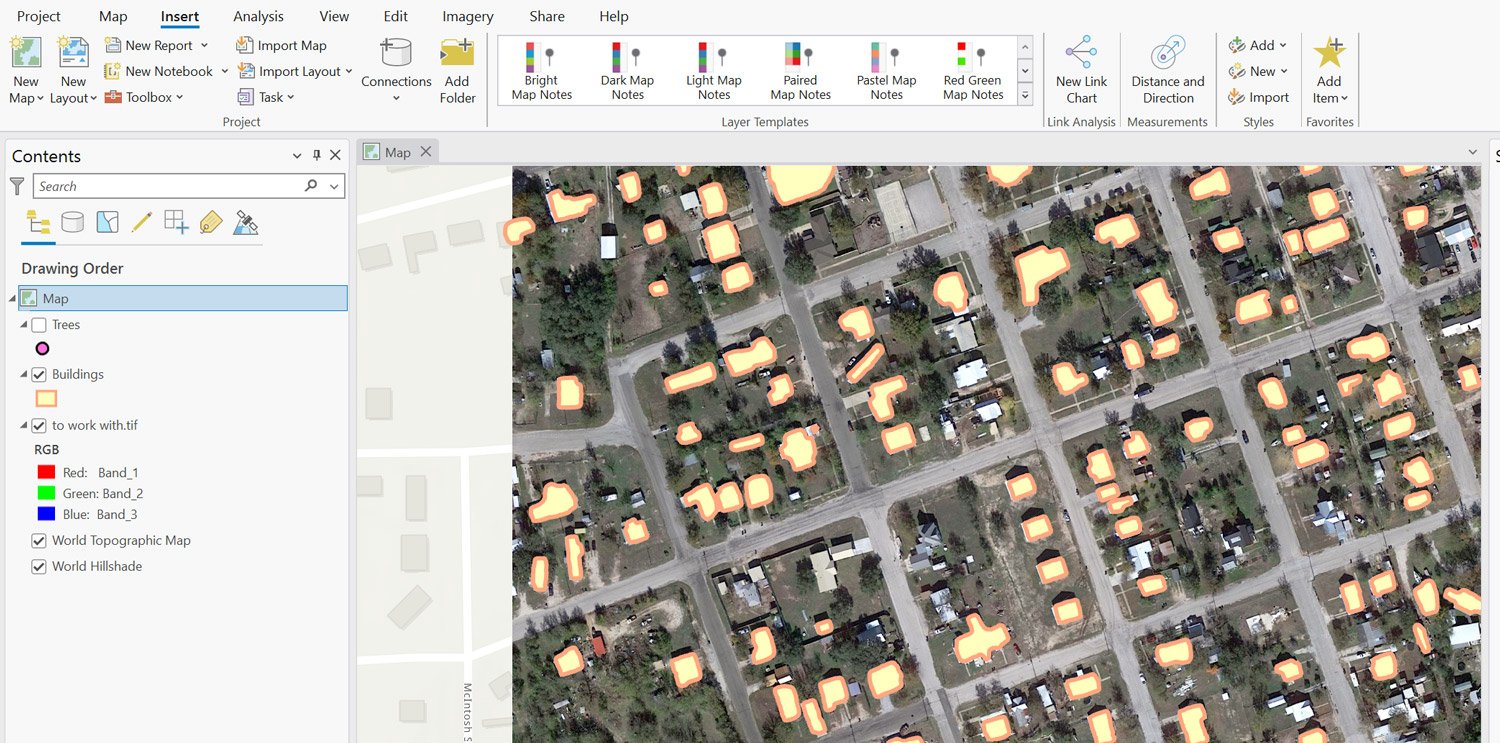
Extracting trees from satellite imagery
You will first need to install the deep learning libraries for ArcGIS Pro by using the link attached. Be sure to retrieve a version compatible with your ArcGIS Pro version.
- Open and create a new project in ArcGIS Pro.
- Select Add data from the Map tab and toggle to the location of the extracted google satellite imagery.
- Click Ok.
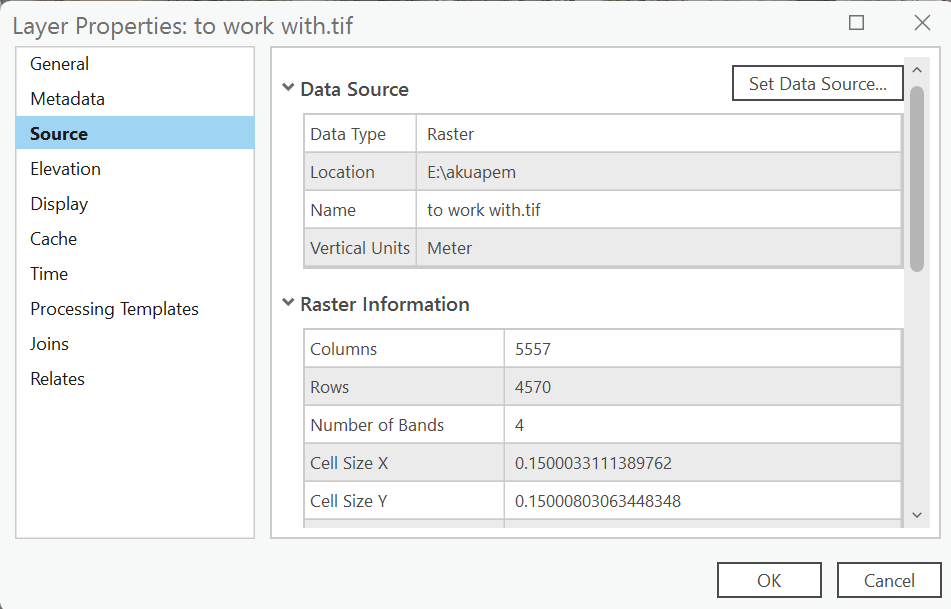
- Once imported check the resolution of the imagery by Right-clicking on the Google satellite layer from the Table of Contents.
- Select Properties.
- Select the Source tab.
- Open the Raster information to view the Cell size X and Y information of the data.
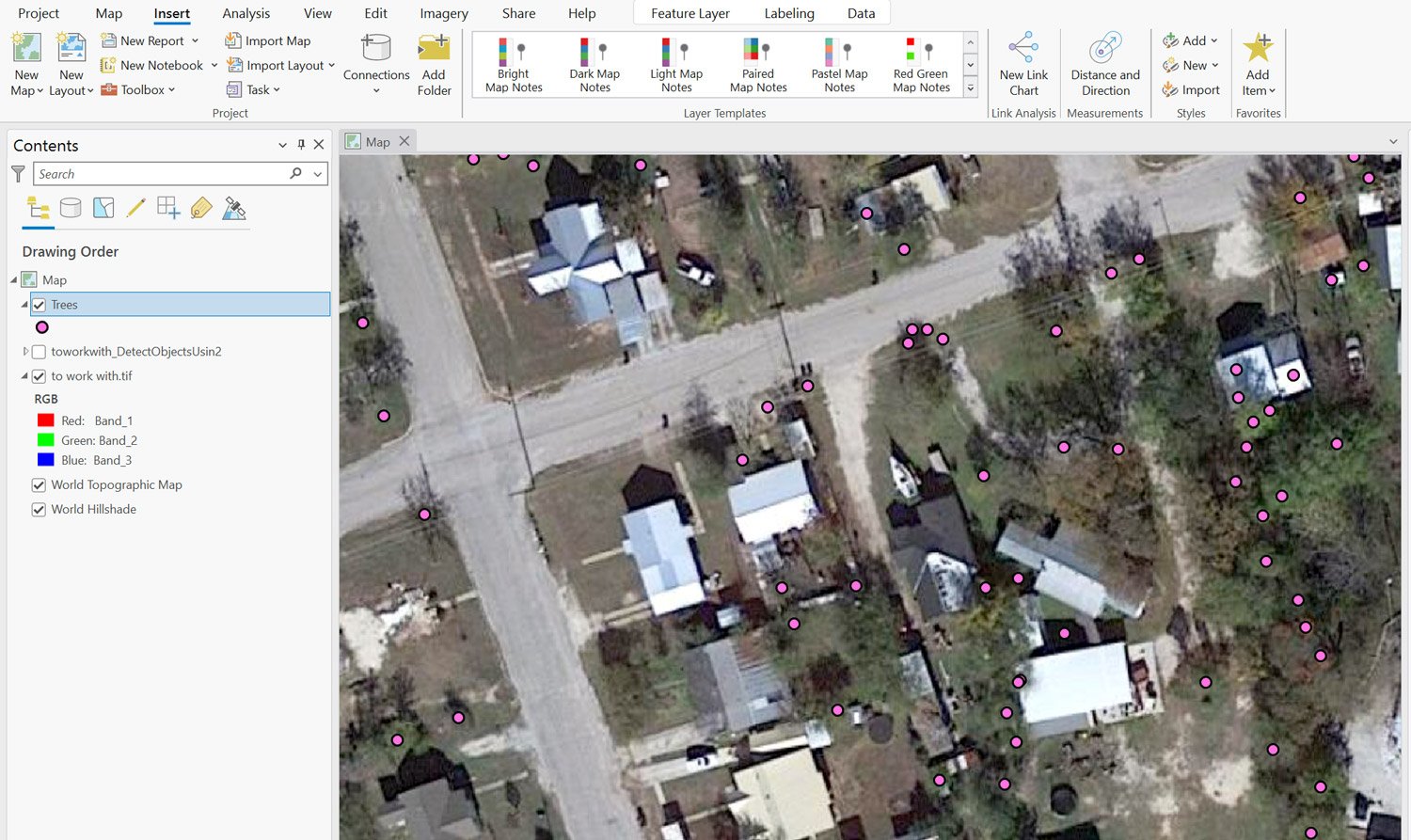
To extract trees from the imported imagery;
- Type and search “detect objects using deep learning” in the search bar of the geoprocessing toolbox.
- Set input raster to the google satellite image.
- Set output detected objects to the output name and location of choice.
- Retrieve the tree detection model file from ArcGIS.com.
- Set model definition to the tree detection.dplk file.

- From the Environments tab, Set processing extent to as specified below.
- Set the processing extent to “Current Display Extent.”
- Set Cell size to 0.150003311138976.
- Set Processing type to GPU.
- Click Run.

You result should be a point layer of identified trees.
Extracting building footprint data from satellite imagery

To extract building footprint data from the imported imagery:
- Type and search “detect objects using deep learning” in the search bar of the geoprocessing toolbox.
- Set input raster to the Google satellite image.
- Set output detected objects to the output name and location of choice.
- Retrieve the building footprint extraction file from ArcGIS.com
- Set model definition to “building footprint extraction.dplk file.”
- Repeat steps as shown in the tree extraction section of this tutorial to set the Environments tab.
Your end result is a polygon layer of building footprints.